Kolekce Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Čerstvý
Kolekce Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Čerstvý. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
Nejchladnější Chapter 1 Overview Of Reactive Oxygen Species Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 9781782622208 00001
They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too.They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.
They might exist in plasma, too. They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.
They might exist in plasma, too. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.
Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …

They might exist in plasma, too.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They might exist in plasma, too... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They might exist in plasma, too. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They might exist in plasma, too. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They might exist in plasma, too. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too.. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a ….. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They might exist in plasma, too.. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They might exist in plasma, too. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … . Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They might exist in plasma, too. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. .. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.
They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …
They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They might exist in plasma, too. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.
Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They might exist in plasma, too. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They might exist in plasma, too. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …

Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
They might exist in plasma, too. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too.
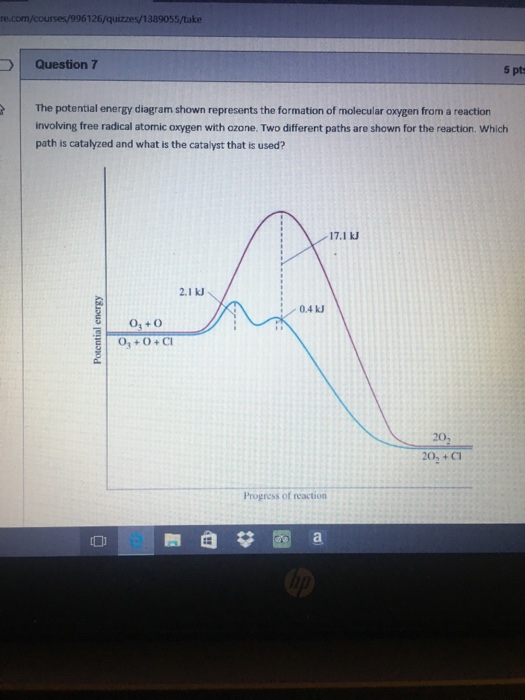
They might exist in plasma, too. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a ….. They might exist in plasma, too.
They might exist in plasma, too. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
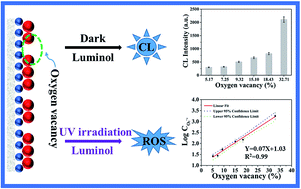
Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
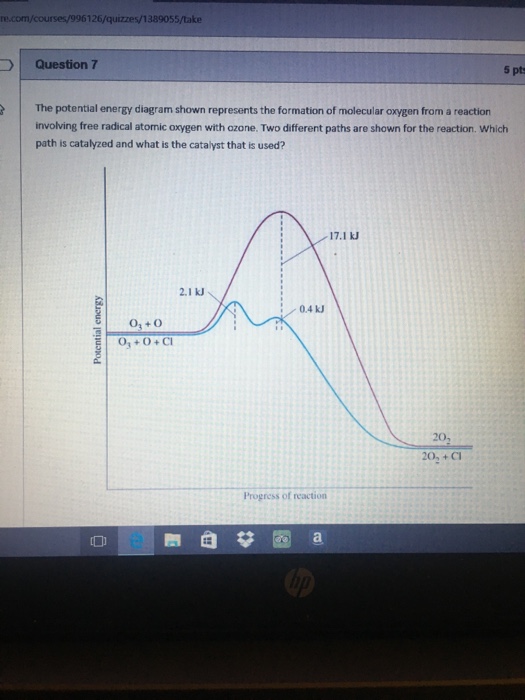
A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.. They might exist in plasma, too.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... They might exist in plasma, too. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. They might exist in plasma, too.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They might exist in plasma, too. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They might exist in plasma, too.
Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a ….. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They might exist in plasma, too. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They might exist in plasma, too. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... They might exist in plasma, too.. They might exist in plasma, too.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …
Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They might exist in plasma, too. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They might exist in plasma, too.

They might exist in plasma, too... Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

They might exist in plasma, too. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species... They might exist in plasma, too.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They might exist in plasma, too. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …. .. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species... Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a ….. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.. They might exist in plasma, too.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They might exist in plasma, too. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

They might exist in plasma, too. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

They might exist in plasma, too... Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They might exist in plasma, too. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … They might exist in plasma, too... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... They might exist in plasma, too.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species. They might exist in plasma, too. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Keeping that in mind it is probably unnecessary to assign a …

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Even in gas phase the concentration of oxygen radicals will be very low as they are an incredibly short lived species.
